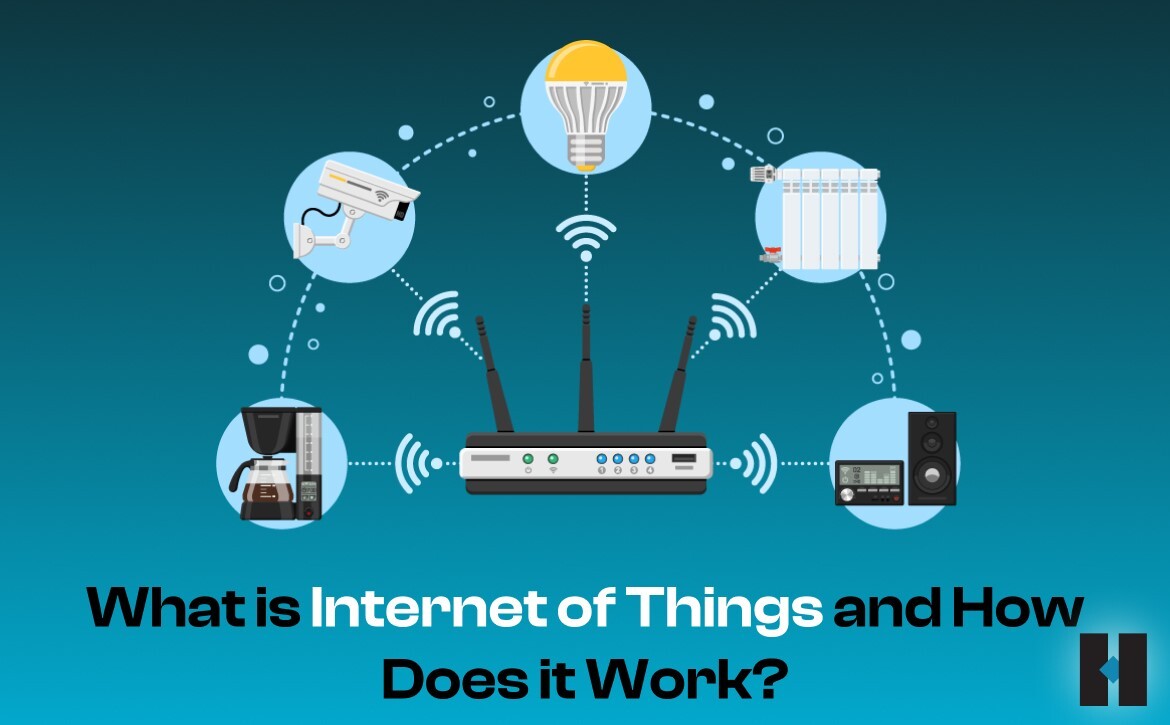
Did you ever imagine that things such as our smartphones, TVs, refrigerators, and cars would be able to talk to each other?
Well, welcome to the world of all things Internet, or IoT in short.
Better known as the Internet of Things, it is the network of internet-friendly devices that can communicate and exchange data with each other.
In a broader sense, it includes every device, machine, or appliance that has some form of software or sensor in it that can capture and monitor your data and transfer it to other devices with the same capabilities.
These devices known to us as smart systems can range from simple home appliances to electronic gadgets to industrial-grade equipment and machines.
In what is called Machine-to-Machine or M2M communication, these devices and machines can connect and communicate with each other in real time without the need for human intervention.
That is, once connected they can automatically transmit your data to other devices even when you are on the go. Being in sync with each other helps you control and operate these devices remotely no matter where you are.
For instance, turning your smart geyser on through a mobile app when you’re about to reach home and need a shower as soon as you get there. Thus saving time and effort for manual control.
There are plenty of other examples in our day-to-day lives and even more benefits of IoT for businesses as a whole that we shall get familiar with in this post. But first!
What Does IoT Mean?
IoT stands for Internet of Things. As a self-explanatory term, it refers to a common network of things and devices through which they can communicate with each other.
Also known as the Internet of Everything or IoE, it is an interconnected ecosystem of several smart devices and sensory objects such as smart lights, smart home systems, smartphones, smartwatches, and so on.
A few other examples include coffee machines, microwaves, geysers, vacuum cleaners, fire alarms, air conditioners, cars, etc.
The point is being on a shared system allows these devices to monitor, collect, assess, and report your behavior and activity across other devices for easy access to your information from any other device that is at your disposal at a given time.
For example, extracting the travel history from your car to your smartphone without having to manually transfer the details. Or check the live feed of the CCTV installed on your property.
And that’s just for appetizers. Specifically, there are about as many IoT devices in the world as there are people around and the number of IoT platforms has more than doubled in the last four years.
The fact is, that IoT devices are rapidly becoming a part of our highly digitalized lives whether we like it or not. And it’s in our great interest to learn these technologies well before they have taken complete control over our lives, now that we have time.
How Does IoT Work?
IoT systems are largely based on sensors and receptors that can observe or sense their immediate surroundings, movements, workings, and user details.
While continuously collecting huge chunks of data, these IoT-enabled devices regularly transmit it across a server or cloud which in turn sends relevant data or instructions back to the device.
For example, a health app or sleep app telling you to drink water or go to bed.
The details or data gathered on a central server can also be easily accessed via a mobile phone or computer from anywhere around the clock.
Here’s how it works:
- Data collection- Sensor-based IoT systems capture the data.
- Cloud connection- IoT devices constantly share that data with the connected server or cloud.
- Data processing and analytics- As part of the IoT platform, these cloud servers and databases analyze the data for meaningful insights.
- Data exchange- The platform then sends these meaningful insights and important details back to the device.
- Recommendations through a user-friendly interface- Finally, the data is shared with other IoT devices in the same network for an enhanced user experience.
And the cycle continues!
Moving on, all these fascinating things and more that IoT devices can do are merely a reflection of their internal components and processes.
Let’s understand that better.
Components of IoT
The technology of IoT is based on several factors such as the types of devices, processing speed, and internet connectivity.
Given the best of these conditions, 4 major components of IoT are commonly found across all the IoT devices and platforms.
These include:
1. Sensors or IoT devices such as smartphones, smartwatches, GPS trackers, motion sensors, microphones, and cameras that can collect and send the data to a server for further processing.
The purpose of these sensors is to observe the changes in the surroundings and the user’s activities to better understand the physical environment and function accordingly.
2. Connectivity is perhaps the most important ingredient in making these IoT devices work in the first place.
Just so you know, smart devices aren’t so smart after all should you take the internet away!
Therefore, to establish a proper connection between IoT devices and IoT servers such as clouds and other data storage servers collectively known as IoT platforms is of utmost importance. To ensure non-stop connectivity, you can use any connectivity technology such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, cellular networks, and so on.
3. Data Processing is yet another integral part of IoT technology. This is where cloud servers and other IoT platforms will do their magic by processing and analyzing large chunks of data in an instant.
Upon analyzing the data, these processors would mine meaningful information and insights that can be sent back to the user or end device for further collaboration and response.
In other words, what a user should do or not, or if there are any changes that he should make or not to make the most out of their IoT applications and appliances.
4. User interface is the final component of an IoT-enabled device as the only thing that matters when it comes to interacting with the end-user.
Better referred to as the product app, it is the user-friendly interface that lets you check and monitor your activity and make necessary changes in your life or the product’s usage as recommended by the app.
Speaking of which, the applications of IoT are not limited to individual use only. There are multiple benefits of IoT for businesses that are equally awe-inspiring.
Applications of IoT in Organisations
IoT has touched almost every aspect of our lives and businesses are no different either.
With an extensive and diverse range of applications, IoT is already on par with some of the coolest technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) that are helping businesses and B2B clients in various industries and sectors.
While showing immense potential in several fields such as healthcare, retail, education, agriculture, travel, finance, housing, and so on, IoT promises many applications at present.
- Asset management.
- Predictive maintenance.
- Manufacturing and Supply chain.
- Energy and resource management.
- Remote viewing/ control.
- Smart infrastructure/ architecture.
- Health and safety hazards.
- Data analytics.
- Regulatory Compliance.
- Customer service and user experience (UX).
Aside from that, other future trends of IoT are on the horizon ready to shine the light.
Future trends of IoT:
- Edge computing.
- 5G integration.
- AI and Machine learning.
- Blockchain.
- Interoperability.
- Security.
- Sustainable solutions (such as harnessing renewable energy).
- Context-aware IoT applications.
- Telemedicine and virtual healthcare.
- Automation and autonomous IoT technologies.
FAQs
Q 1. Can IoT work without the Internet?
Ans: Although the internet is often required to use IoT devices, especially in terms of data storage, analysis, and remote access; they can still work without the internet in what is called “Offline or Local IoT.” Examples include Local Network Communication, edge computing, P2P connection, etc.
Q 2. What are the uses of IoT?
Ans: There are tons! Some of the most common include:
- Smart home automation
- Industrial grade IoT
- Health monitoring
- Smart Agriculture and farming
- Smart cities
- Retail analysis
- Energy conservation
- Supply chain
- Environmental sustainability
- Transport management
Q 3. What are examples of IoT devices?
Ans: IoT devices come in several forms and with several purposes with a diverse range of applications. Here are the most easily seen examples of IoT-connected devices from our day-to-day lives:
- Smart wearables such as smartwatches and fitness trackers.
- Smart home systems and virtual assistants such as Alexa and Siri.
- CCTVs and security cameras.
- Smart lights and lighting systems.
- Smart locks and alarms.
- Smart home appliances.
- Sensor-based devices such as vacuum cleaners.
- Industrial grade sensors such as agriculture sensors.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs) and modern cars.
Q 4. What are IoT devices?
Ans: IoT devices are those physical objects, devices, and equipment that are embedded with softwares, sensors, and other technologies to collect and share data over the internet. For example, smartwatches and smartphones.
Q 4. What is the future of IoT?
Ans: IoT is a promising technology that continues to baffle innovators and users alike. While it has dozens of applications for both consumers and businesses, the future of IoT depends largely on the optimization of sensor processing. With better computing power and data processing speed, IoT can help us build a better world with better smart cities.